General Chemistry/Ionic bonds
What are ions?
Ions are atoms or molecules which are electrically charged. Cations are positively charged and anions carry a negative charge. Ions form when atoms gain or lose electrons. Since electrons are negatively charged, an atom that loses electron(s) will become positively charged (similarly an atom that gains one or more electrons becomes negatively charged).
Description of Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonding are the attraction between positive and negative charged ions. These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form three dimensional ionic networks (or lattices). Electrostatics explains why this happens: opposite charges attract and like charges repel. When many ions attract each other, they form large, ordered, crystal networks/lattices in which each ion is surrounded by ions of the opposite charge. Generally, when metals react with non-metals, electrons are transfered from the metals to the non-metals. The metals form positively charged ions and the non-metals form negatively charged ions. The smallest unit of an ionic compound is the formula unit.
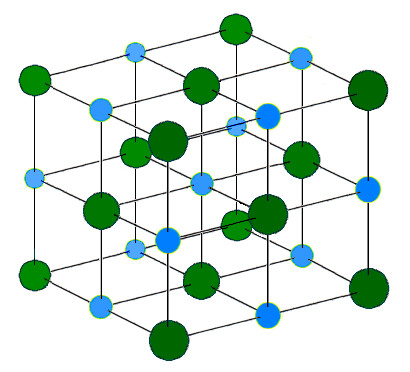
Characteristics
.
Ionically bonded substances typically have the following characteristics.
- High melting point (solid at room temp)
- Brittle (can shatter)
- Some dissolve in water
- Conduct electricity when dissolved or melted
Formation

Ionic bonds form when metals and non-metals chemically react. By definition, a metal is relatively stable if it loses electrons to form a complete valence shell and becomes positively charged. Likewise, a non-metal is relatively happy to gain electrons to complete its valence shell and become negatively charged. When metals and non-metals react, the metals lose electrons by transferring them to the non-metals, which gain them. Consequently, ions are formed, which instantly attract each other - ionic bonding.
For instance in the reaction of Na (sodium) and Cl (chlorine), each Cl atom takes one electron from a Na atom. Therefore each Na becomes a Na+ cation and each Cl atom becomes a Cl- anion. Due to their opposite charges, they attract each other to form an ionic network/lattice. The formula (ratio of positive to negative ions in the network/lattice is NaCl
It should also be noted that some atoms can form different types of ions. For instance Fe (iron) can become Fe2+ (or ironII or ferrous). Fe can also become Fe3+ (a.k.a. ironIII or ferric). hv