Fractals/Iterations in the complex plane/Julia set
This book shows how to code diffrent algorithms for drawing sets in dynamical plane : Julia, Filled-in Julia or Fatou sets for complex quadratic polynomial.
Escape time
Basin of attraction to infinity = exterior of filled-in Julia set
Here one comutes forward iterations of Z point :
Here is C++ function which computes last iteration for iteration of complex quadtratic polynomial. It is a iteration ( integer) for which (abs(Z)>EscapeRadius).
int GiveLastIteration(complex C,complex Z , int imax, int EscapeRadius)
{
int i; // iteration number
for(i=0;i<=imax-1;i++) // forward iteration
{
Z=Z*Z+C; // overloading of operators
if(abs(Z)>EscapeRadius)break;
}
return i;
}
Boolean Escape time

Algorithm: for every point z of dynamical plane (z-plane) compute iteration number ( last iteration) for which magnitude of z is greater then escape radius. If last_iteration=max_iteration then point is in filled-in Julia set, else it is in its complement(attractive basin of infinity ). Here one has 2 options, so it is named boolean algorithm.
if (LastIteration==IterationMax) then color=BLACK; /* bounded orbits = Filled-in Julia set */ else color=WHITE; /* unbounded orbits = exterior of Filled-in Julia set */
In theory this method is for drawing Filled-in Julia set and its complement ( exterior), but when c is Misiurewicz point ( Filled-in Julia set has no interior) this method draws nothing. It means that it is good for drawing interior of Filled-in Julia set .
Integer escape time = Level Sets of the Basin of Attraction of Infinity = Level Sets Method= LSM/J
Escape time measures time of escaping to infinity ( infinity is superattracting point for polynomials). Time is measured in steps ( iterations) needed to escape from circle of given radius ( ER= Escape Radius).
Level sets here are sets of points with the same escape time. Here is algorithm of choosing color in black & white version.
if (LastIteration==IterationMax)
then color=BLACK; /* bounded orbits = Filled-in Julia set */
else /* unbounded orbits = exterior of Filled-in Julia set */
if ((LastIteration%2)==0) /* odd number */
then color=BLACK;
else color=WHITE;
Level Curves of escape time Method = LCM/J
Algorithm is based on paper by M. Romera et al.[1]
Escape time for finite attractor - interior of filled-in Julia set

Decomposition of level sets
Binary decomposition
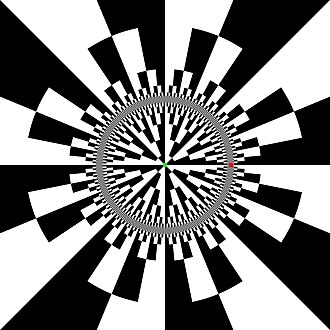
Binary decomposition of basin of attraction of infinity (algorithm in pseudocode) :
if (LastIteration==IterationMax)
then color=BLACK; /* bounded orbits = Filled-in Julia set */
else /* unbounded orbits = exterior of Filled-in Julia set */
if (Zy>0) /* Zy=Re(Z) */
then color=BLACK;
else color=WHITE;
Inverse Iteration Method = IIM/J


In escape time one computes forward iteration of point z.
In IIM/J one computes:
- repelling fixed point of complex quadratic polynomial
- preimages of by inverse iterations
Because square root is multivalued function then each has two preimages . Thus inverse iteration creates binary tree.
Variants of IIM
- random choose one of two roots ( up to chosen level )= random walk through the tree.
- both roots with the same probability
- more often one then other root
- draw some rare paths in binary tree = MIIM
- draw all roots ( up to chosen level ). There are some posible way to go through all the tree. It is implemented in Fractint[2].
Here is Maxima code for simple IIM:
finverseplus(z,c):=sqrt(z-c); finverseminus(z,c):=-sqrt(z-c); c:%i; /* define c value */ iMax:5000; /* maximal number of reversed iterations */ fixed:float(rectform(solve([z*z+c=z],[z]))); /* compute fixed points of f(z,c) : z=f(z,c) */ if (abs(2*rhs(fixed[1]))<1) /* Find which is repelling */ then block(beta:rhs(fixed[1]),alfa:rhs(fixed[2])) else block(alfa:rhs(fixed[1]),beta:rhs(fixed[2])); z:beta; /* choose repeller as a starting point */ /* make 2 list of points and copy beta to to lists */ xx:makelist (realpart(beta), i, 1, 1); /* list of re(z) */ yy:makelist (imagpart(beta), i, 1, 1); /* list of im(z) */ for i:1 thru iMax step 1 do /* reversed iteration of beta */ block (if random(1.0)>0.5 then z:finverseplus(z,c) else z:finverseminus(z,c), xx:cons(realpart(z),xx), /* save values to draw it later */ yy:cons(imagpart(z),yy) ); plot2d([discrete,xx,yy],[style,[points,1,0,1]]); /* draw reversed orbit of beta */
Compare it with C code.
Complex potential
CPM/J
External angle
BSM/J
DEM/J
Internal distance estimation
External distance estimation

Algorithm for computing distance from point z ( in exterior ) to nearest point on the boundary of Julia set. Here is pseudocode:
if (LastIteration==IterationMax)
then { /* interior of Julia set: color = black */ }
else /* exterior of Filled-in Julia set */
{ double distance=give_distance(Z0,C,IterationMax);
if (distance<distanceMax)
then { /* Julia set : color = white */ }
else { /* exterior of Julia set : color = black */}
}
So one have to compute distance using formula :
where :
is first derivative with respect to c and is computed using iteration :
DistanceMax is smaller then pixel size. One can start with DistanceMax=pixel_size and if the result is not good change DistanceMax=pixel_size/n where n is number greater then 1.
Computing periodic points in Maxima
Define c value
(%i1) c:%i; (%o1) %i
Fixed points ( period = 1 )
Compute fixed points
(%i2) p:float(rectform(solve([z*z+c=z],[z]))); (%o2) [z=0.62481053384383*%i-0.30024259022012,z=1.30024259022012-0.62481053384383*%i]
Find which is repelling :
if (abs(2*rhs(p[1]))<1)
then block(
beta:rhs(p[1]),
alfa:rhs(p[2])
)
else block(
alfa:rhs(p[1]),
beta:rhs(p[2])
);
Show alfa type fixed point:
(%i20) alfa; (%o20) 0.62481053384383*%i-0.30024259022012
Show beta type fixed point:
(%i21) beta; (%o21) 1.30024259022012-0.62481053384383*%i
Show that sum of alfa and beta is 1
(%i10) p:solve([z*z+c=z], [z]); (%o10) [z=-(sqrt(1-4*%i)-1)/2,z=(sqrt(1-4*%i)+1)/2] (%i14) s:radcan(rhs(p[1]+p[2])); (%o14) 1
Draw points :
(%i15) xx:makelist (realpart(rhs(p[i])), i, 1, length(p)); (%o15) [-0.30024259022012,1.30024259022012] (%i16) yy:makelist (imagpart(rhs(p[i])), i, 1, length(p)); (%o16) [0.62481053384383,-0.62481053384383] (%i18) plot2d([discrete,xx,yy], [style, points]);
One can add point z=1/2 to the lists:
(%i31) xx:cons(1/2,xx); (%o31) [1/2,-0.30024259022012,1.30024259022012] (%i34) yy:cons(0,yy); (%o34) [0,0.62481053384383,-0.62481053384383] (%i35) plot2d([discrete,xx,yy], [style, points]);
period 2 points
(%i2) solve([(z*z+c)^2+c=z], [z]); (%o2) [z=-(sqrt(-4*c-3)+1)/2,z=(sqrt(-4*c-3)-1)/2,z=-(sqrt(1-4*c)-1)/2,z=(sqrt(1-4*c)+1)/2]
Show that z1+z2 = -1
(%i4) s:radcan(rhs(p[1]+p[2])); (%o4) -1
Show that z2+z3=1
(%i6) s:radcan(rhs(p[3]+p[4])); (%o6) 1
Finding period of orbit


Color
3D
More tutorials and code
- in Basic see Mandelbrot Dazibao
- in Java see Evgeny Demidov
- in C see :
- in C++ see Wolf Jung page,
- in Lisp for Maxima see Dynamics by Jaime E. Villate
- in Mathemathica see :